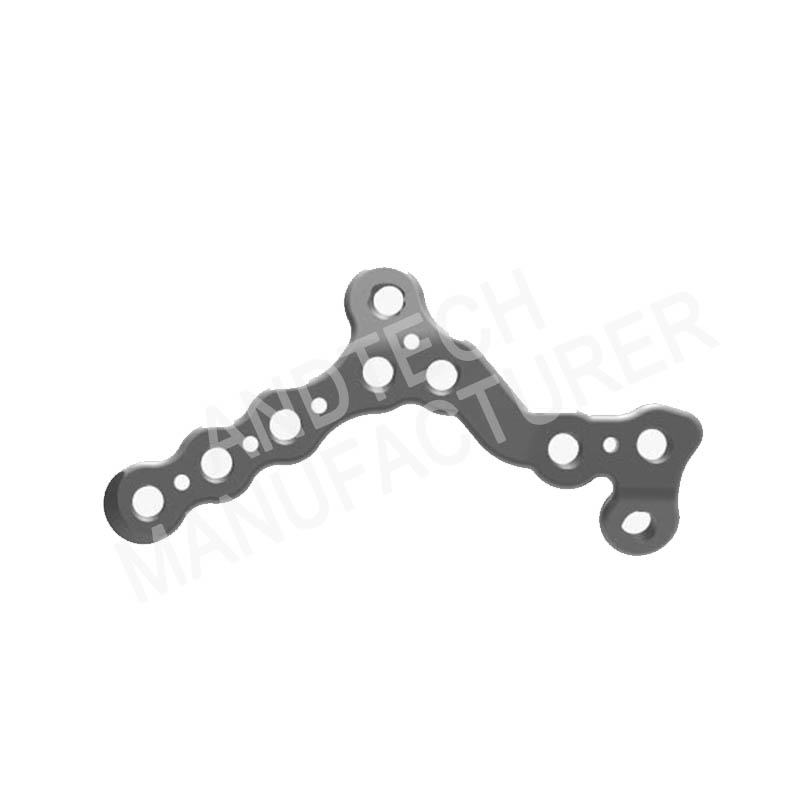
Various Kinds Of Calcaneal Locking Plate
Features of calcaneal fractures
Calcaneal fractures are the most common tarsal fractures, accounting for approximately 2% of all fractures. Improper treatment of calcaneal fractures can cause malunion of calcaneal fractures, resulting in changes such as heel widening, height reduction, flat foot deformity, and varus or valgus feet. Therefore, restoring the normal biomechanical anatomy and function of the hindfoot has become one of the main goals of the treatment of calcaneal fractures.
The most common tarsal fractures, accounting for 60% of tarsal fractures, accounting for 2% of systemic fractures, about 75% of intra-articular fractures, 20% to 45% associated with calcaneocuboid joint injury.
Due to the complex anatomical structure of the calcaneus and surrounding areas, the quality of local soft tissue coverage is poor, and there are many sequelae and poor prognosis.
The treatment plan is highly individualized, and the methods are not uniform.
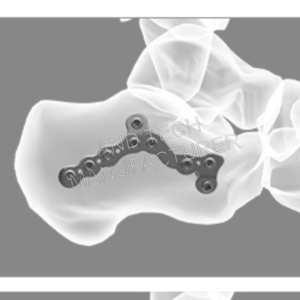
combined calcaneal locking plate
Posterior calcaneal tuberosity locking plate
Code: 251516XXX
Screw Size: HC3.5
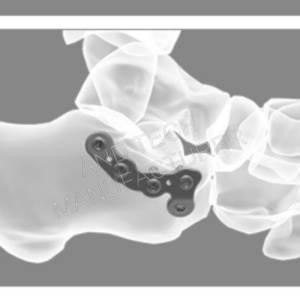
Code: 251517XXX
Screw Size: HC3.5
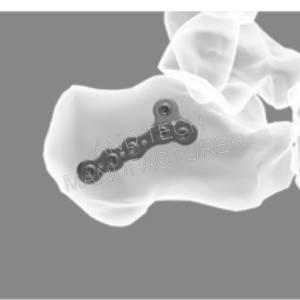
Calcaneus protrusion locking plate
Code: 251518XXX
Screw Size: HC3.5
Calcaneal fracture classification
●Type I: nondisplaced intra-articular fracture;
●Type II: The posterior articular surface of the calcaneus is a two-part fracture with a displacement > 2mm. According to the position of the primary fracture line, it is divided into Type IIA, IIB, and IIC;
●Type III: There are two fracture lines on the posterior articular surface of the calcaneus, which is a three-part displaced fracture, which is further divided into type IIIAB, IIIBC, and IIIAC;
●Type IV: Displaced fractures with four or more parts on the posterior articular surface of the calcaneus, including comminuted fractures.
Indications:
Fractures of the calcaneus including, but not limited to, extraarticular,intraarticular, joint depression, tongue type, and multifragmentary fractures.











