The patient is a 62-year-old female
Preoperative diagnosis:
1. Left foot 2 diabetic foot with Wanger grade 3 infection
2. Type 2 diabetes with peripheral vascular, neuropathy
3. Type 2 diabetes with vasculitis
4. Grade 2 hypertension, very high risk, coronary heart disease
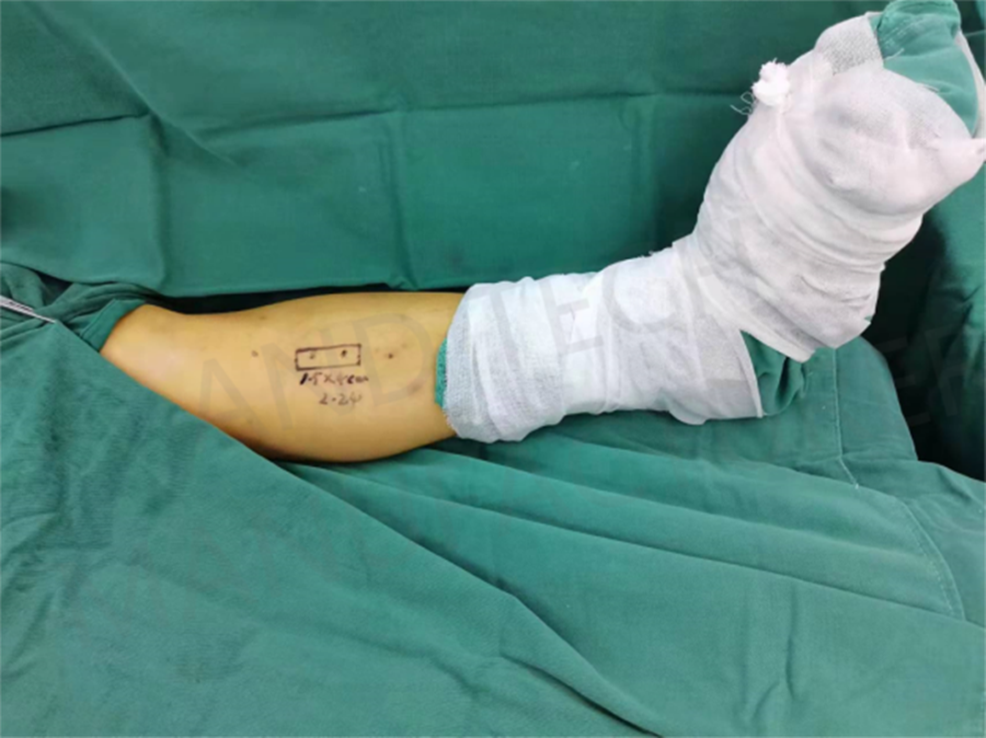
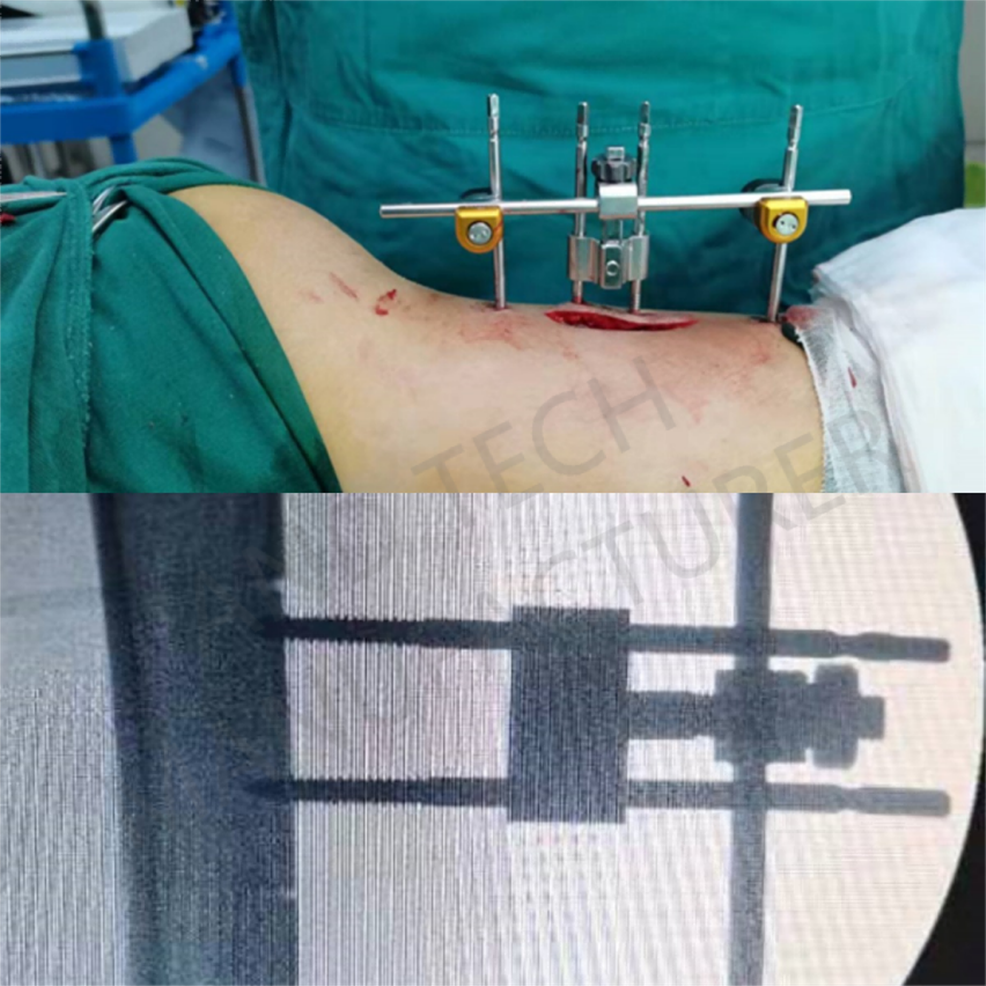
The patient's left upper tibia underwent lateral bone transfer with osteotomy and external fixator, and the osteotomy range was 1.5cm×4cm
Diabetic foot refers to the reduction of blood flow (poor circulation) to the legs and feet in the presence of diabetes, which can lead to a difficult-to-heal foot ulcer or infection.
Because people with diabetes are more likely to develop peripheral arterial disease (PAD), which causes the arteries to become narrowed or blocked.
Chronic high blood sugar can lead to nerve damage in diabetic neuropathy. Diabetic neuropathy can occur throughout the body, but is most common in the legs and feet.
If your feet are numb, you may not notice blisters, cuts, or pain. For example, you may not even feel that a pebble in your sock will cut your foot. Unnoticed and untreated wounds can become infected.
If not treated quickly, diabetic foot ulcers or blisters can become infected. Sometimes a surgeon must amputate (remove) a toe, foot, or part of the leg to prevent the infection from spreading.
People with diabetes have about a 15% chance of developing a diabetic foot at some point in their life.
Post time: Mar-08-2022





