Surgical methods
After admission, patients were treated with staged surgical treatment depending on the situation. First, the external fixator was fixed, and if the soft tissue conditions allowed, it was replaced with internal fixation.
The authors summed up their experience and found that the key to fracture reduction and reduction maintenance is to reduce the posterior cortical fracture of the tibia first, and then deal with the compression fracture of the anterior tibial plateau, so as to restore the normal sagittal plane line.
The authors recommend the use of proximal tibial anterolateral and posteromedial approaches for fracture reduction and fixation.
The posterior tibial approach can be used to expose the posterior structure of the tibia and perform reduction and anteromedial support plate fixation during the operation.
In addition, temporary fixation of posterior tibial plateau fractures may serve as a fulcrum to lift the anterior fracture and reduce fracture displacement during subsequent correction of the sagittal alignment.
Once the posterior fracture reduction is completed, a temporary fixation device should be used for fixation, such as a 1/3 tubular plate or a 3.5mm screw from the anterior distal end to the posterior proximal end.
Next, restore the alignment of the tibial plateau articular surface and sagittal plane. During the operation, use a reduction device with a wider tip to reduce the pressure and avoid the aggravation of fracture comminuted.
Restoration of posterior tibial inclination was initiated with an anterior flap spacer or an osteotome simultaneously (Fig. 2). Below the proximal joint line, multiple Kirschner wires were inserted in parallel from front to back, and the tibial retroversion was restored by lifting the Kirschner wires, and then fixed on the posterior cortex.
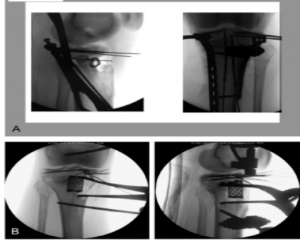
A- Fibular head autograft; B- Spinal Cage filling bone defect
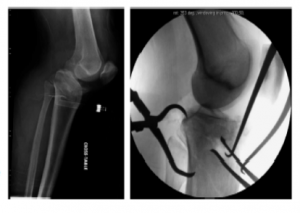
The lateral X-ray shows sagittal deformity, and the right plain film shows reduction forceps to reduce the posterior tibial fracture with the aid of the sheet space distractor
Finally, the plate was used to reduce the fracture fragment to correct the sagittal retroversion. The proximal end of the proximal lateral tibial plate (locking or non-locking) should be parallel to the articular surface, and the distal end should be slightly posterior. The plate was fixed to the proximal fragment with screws, and then the plate and the proximal fragment were reduced and fixed on the tibial shaft by fixing the distal plate, so as to restore the normal tibial posterior inclination.
Once the fracture reduction is completed, temporary fixation with Kirschner wires can be used. In some cases, stable temporary fixation is difficult to perform without first restoring the line of force with a graft (tricortical iliac graft, fibular head graft, etc.)
Post time: May-09-2022





