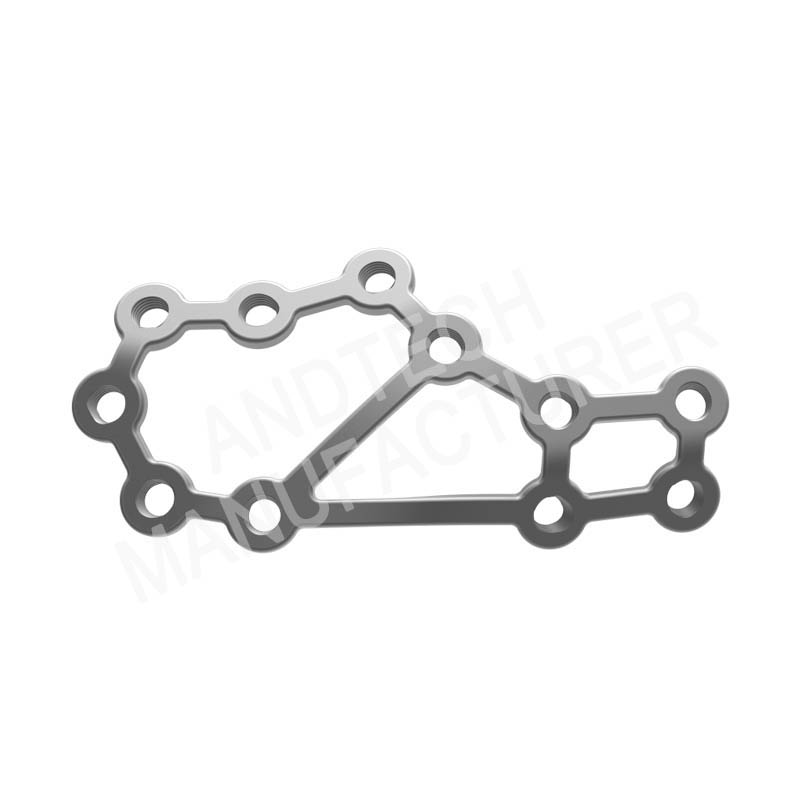
Calcaneal Locking Plate III
The calcaneus, the largest of the seven tarsal bones, is located on the lower back of the foot and forms the heel (heel of the foot)
Calcaneal fractures are relatively rare, accounting for 1% to 2% of all fractures, but are important because they can lead to long-term disability. The most common mechanism of severe calcaneal fractures is axial loading of the foot after a fall from a height. Calcaneal fractures can be divided into two categories: extra-articular and intra-articular. Extra-articular fractures are often easier to assess and treat. Patients with calcaneal fractures often have multiple comorbid injuries, and it is important to consider this possibility when evaluating patients
The subcutaneous soft tissue on the medial surface of the calcaneus is thick, and the bone surface is arc-shaped depression. The middle 1/3 has a flat protrusion, which is the load distance protrusion
Its cortex is thick and hard. The deltoid ligament is attached to the talar process, which is attached to the navicular plantar ligament (spring ligament). Vascular nerve bundles pass through the inside of the calcaneus